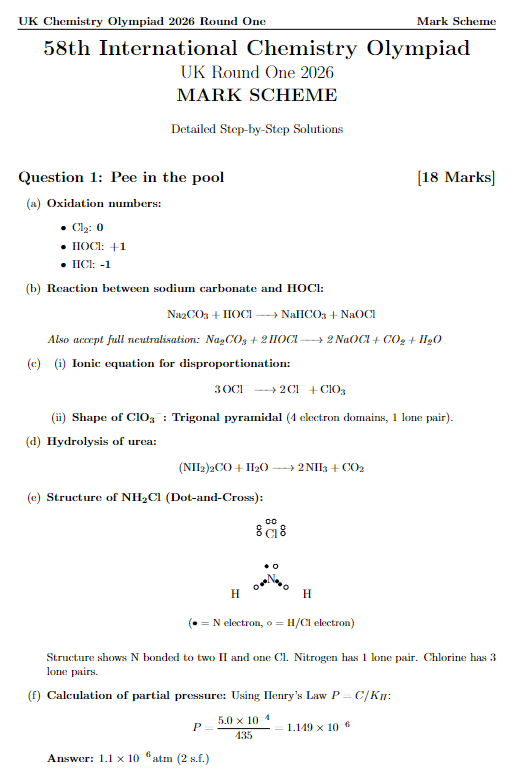
英国伯明翰大学地理、地球与环境科学学院招收全奖博士
采矿岩溶石灰岩集水区中四维地下水流动分布的确定
关于项目
鉴于岩溶石灰岩集水区中水流在空间和时间上通常具有显著变异性,量化其水流运动颇具挑战性(Bodin等人,2022)。这种变异性在很大程度上受到岩溶发育程度(即溶解作用增强的管道发育)以及由此导致的人为空间尺度上岩溶岩体高度非均质性的影响。通常,此类系统表现出明显的非平稳和非线性水文特征(Banusch等人,2002;Gunn & Bradley,2023;2024)。若石灰岩风化形成“幽灵岩”地下水系统(Dubois等人,2014),则情况更为复杂。
在此类系统中,已有既定方法可量化补给和排泄速率,且常采用示踪试验来确定离散补给点和排泄点之间的联系。然而,一个重要的普遍不确定性在于离散输入点和输出点之间的实际路径,特别是深层地下水流动情况,这一问题在研究文献中多有讨论(如Kaufmann等人,2014),但与其他问题相比,综合研究相对较少。从实际角度来看,确定水流分布对于环境保护工作和深层工程项目都至关重要。
因此,本博士项目的目标是开发一种方法,以确定岩溶石灰岩集水区中三维水流分布,以及这些分布在时间上的变化。这一目标虽具挑战性,但若能成功实现,将带来巨大回报。
研究方法将结合对英国峰区石炭纪石灰岩研究集水区的实地和数值模拟实验。本项目之所以能够开展,得益于可进入一个大型深石灰岩采石场:尽管采矿会对水流系统产生显著影响(如Green等人,2003;Hobbs & Gunn,1998;Hobbs,2014;Lolcama等人,2002),但同时也为研究提供了重要机遇。研究集水区内的采石场拥有数十年来收集的异常广泛的数据集,包括水位、流量和示踪试验数据。此外,近期还钻探了深钻孔,以探索采石场基底以下的水流系统。项目将提供探地雷达、水文地质现场化学和液压测试设备、无人机、摄影测量软件以及专业地下水流动软件(如Baggett等人,2019;Borghi等人,2016;Jeannin等人,2021)的使用权限。研究者将得到一个专门组建的大型导师团队的支持,该团队具备与本多学科项目各方面相匹配的专业知识。
我们正在寻找一位热情、勤奋的研究者,其需具备原创性思维能力,且至少在地球科学、工程学、“纯”科学和数学等广泛领域中的一个领域有专业背景。研究者需参与实地工作和分析,包括数值模拟。导师将根据研究者的背景提供培训:此外,研究者还可修读大学的“水文地质学”理学硕士课程。
资助说明
本博士项目在合同最终确定后,将由英国西麦斯运营有限公司(CEMEX UK Operations Limited)全额资助,为期3.5年。英国学生的大学注册费由资助方承担,但非英国学生需自行筹集资金,以支付英国学生与海外学生注册费之间的差额。资助金在英国研究与创新署(UKRI)资助学生奖学金通常金额的基础上,每年额外提供5000英镑(详见网站apply-for-funding/studentships-and-doctoral-training/get-a-studentship-to-fund-your-doctorate/)。此外,还为实地工作、差旅和食宿以及参加国际会议提供资金支持。
参考文献
Baggett, J, A Abbasi, J Monsalve, R Bishop, N Ripepi, & J Hole. 2019. Ground-penetrating radar for karst detection in underground stone mines. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration,https://doi.org/10.1007/s42461-019-00144-1Banusch, S, M Somogyvari, M Sauter, P Renard, & I Engelhardt. 2002 I. Stochastic modeling approach to identify uncertainties of karst conduit networks in carbonate aquifers. Water Resources Research. 58, e2021WR031710.Bodin, J, G Porel, B Nauleau, & D Paquet. 2022. Delineation of discrete conduit networks in karst aquifers via combined analysis of tracer tests and geophysical data. Hydrology & Earth System Science. 26, 1713–1726.Borghi, A, P Renard, & F Cornaton. 2016. Can one identify karst conduit networks geometry and properties from hydraulic and tracer test data? Advances in Water Resources 90, 99–115.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.02.009Dubois, C., Quinif, Y., Baele, J.-M., Barriquand, L., Bini, A., Bruxelles, L., Dandurand, G., Havron, C., Kaufmann, O., Lans, B., Maire, R., Martin, J., Rodet, J., Rowberry, M.D., Tognini, P. & Vergari, A., 2014. The process of ghost-rock karstification and its role in the formation of cave systems. Earth-Science Reviews, 131, 116–148.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.01.006Green, J., Pavlish, J., Leete, J., and Alexander, Jr., E. 2003. Quarrying Impacts on Groundwater Flow Paths.): Proceedings of the Ninth Multidisciplinary Conference on Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst, 216-222.Gunn, J & C Bradley. 2023. Characterising rhythmic and episodic pulsing behaviour in the Castleton Karst, Derbyshire (UK) using high resolution in-cave monitoring. Water, 15, doi: 10.3390/w15122301Gunn, J & C Bradley. 2024. From recharge to cave to spring: transmission of a flood pulse through a complex karst conduit network, Castleton, Derbyshire (UK). Water, 16, 1306, doi: 10.3390/w16091306Hobbs, SL, & J Gunn. 1998. The hydrogeological effect of quarrying karstified limestone: options for prediction and mitigation. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology, 31: 147-157Hobbs, S. 2014. Deepening of Torr Quarry: Assessing the hydrogeological impacts. p. 100-107 in Hunger, E., Brown, T. J. and Lucas, G. (Eds.), Proceedings of the 17th Extractive Industry Geology Conference, EIG Conferences Ltd. 202pp.Jeannin, P.-Y, G Artigue, C Butscher, Y Chang, J-B Charlier, L Duran, L Gill, A Hartmann, A Johannet, H Jourde, et al 2021. Karst modelling challenge 1: Results of hydrological modelling. Journal of Hydrology, 600, 126508.Kaufmann, G, F Gabrovsek, & D Romanov. 2014. Deep conduit flow in karst aquifers revisited. Water Resour. Res., 50, 4821–4836, doi:10.1002/2014WR015314.Lolcama J L, Cohen H A, Tonkin M J. 2002. Deep karst conduits, flooding, and sinkholes: lessons for the aggregates industry. Engineering Geology 65 (2002) 151–157