Video games have more positiveeffects on children’s developmentthan negative ones.
电子游戏对儿童发展的积极影响大于消极影响。
Background
背景
Video games have become one of the most popular forms of entertainment for children around the world. They range from simple mobile games to complex, immersive experiences on consoles and computers. Many children spend hours each week playing, and parents and teachers are debating whether this is good or bad for development.
电子游戏已成为全球儿童最受欢迎的娱乐形式之一,涵盖从简单手机游戏到主机和电脑端复杂沉浸式体验等多种类型。许多儿童每周花费数小时玩游戏,家长和教师们正就这一现象对儿童发展的利弊展开争论。
Supporters say that video games can have many positive effects. They can improve skills like problem-solving, memory, and hand-eye coordination. Strategy and puzzle games encourage critical thinking, while team-based games teach communication and cooperation. Some games are even designed for education, helping children learn subjects like math or history in a fun way. Games can also provide stress relief and build friendships in online communities.
支持者认为电子游戏具有诸多积极影响:能提升问题解决、记忆力和手眼协调能力;策略类和益智类游戏可激发批判性思维,团队协作类游戏能培养沟通与合作能力;部分教育类游戏还能以趣味方式帮助儿童学习数学、历史等学科;游戏还可缓解压力,并在网络社区中促进友谊建立。
Opponents worry that too much gaming can harm children. Long hours in front of screens may lead to less physical activity, poor sleep, and worse school performance. Violent or addictive games can increase aggression, cause anxiety, or make children spend money irresponsibly. Online gaming also brings risks such as bullying and exposure to harmful content. Critics argue that the negatives often outweigh the positives, especially when gaming is not supervised.
反对者则担忧过度游戏会对儿童造成伤害:长时间面对屏幕可能导致体育活动减少、睡眠质量下降和学习成绩下滑;暴力或成瘾性游戏可能加剧攻击性、引发焦虑,或导致儿童乱花钱;网络游戏还存在霸凌、接触不良内容等风险。批评者认为,尤其是在缺乏监管的情况下,电子游戏的负面影响往往大于积极影响。
This debate asks: Do video games bring more positive effects than negative ones for children’s development? Which side has the stronger impact on learning, health, and social growth in the long run?
本次辩论核心问题:电子游戏对儿童发展的积极影响是否大于消极影响?从长远来看,哪一方对儿童的学习、健康和社交成长影响更为显著?
Key Definitions
核心定义
Video games: Interactive digital games played on consoles, computers, or phones.
电子游戏:可在主机、电脑或手机上运行的交互式数字游戏。
Children’s development: The mental, social, and physical growth of people under 18 years old.
儿童发展:18岁以下人群在心理、社交和身体方面的成长过程。
Positive effects: Benefits such as learning skills, problem-solving, teamwork, or stress relief.
积极影响:包括学习技能、问题解决、团队协作、压力缓解等益处。
Negative effects: Harms such as addiction, poor sleep, aggression, or less exercise.
消极影响:包括成瘾、睡眠不佳、攻击性增强、运动减少等危害。
How to Judge the Debate
(Framework)
辩论评判标准(框架)
We judge the debate by asking 我们通过以下问题评判辩论胜负:
1) Do video games help children learn skills and think more creatively?电子游戏是否有助于儿童学习技能并提升创造力?
2) Do they support or harm children’s health, habits, and well-being?电子游戏对儿童的健康、习惯和幸福感起到促进作用还是损害作用?
3) Do they make children more connected and confident, or more isolated and anxious?电子游戏会让儿童更善于交际、更自信,还是更孤立、更焦虑?
4) Which side shows that the long-term impact of video games is more positive than negative?哪一方能证明电子游戏的长远影响总体上利大于弊?
Context
背景情况
Right now, video games are a central part of many children’s lives. From mobile games to online multiplayer platforms, kids spend hours each week playing. Supporters see games as more than entertainment: they can build problem-solving skills, improve memory and coordination, and even help with teamwork and creativity. Educational games are being used in schools to make learning more engaging.
如今,电子游戏已成为许多儿童生活的核心部分。从手机游戏到在线多人游戏平台,孩子们每周会花费数小时玩游戏。支持者认为游戏不仅是娱乐:还能培养问题解决能力、提升记忆力和协调能力,甚至有助于团队协作和创造力发展。教育类游戏已被应用于学校教学,让学习更具吸引力。
At the same time, many parents and teachers are worried. Long hours of gaming can replace exercise, outdoor play, and study time. Games with violent or addictive designs may cause stress, aggression, or compulsive behavior. Online platforms also bring risks like bullying and exposure to harmful content. In some cases, children’s sleep, school performance, and family relationships are negatively affected.
与此同时,许多家长和教师深感担忧:长时间游戏会挤占运动、户外活动和学习时间;含有暴力元素或设计成瘾的游戏可能引发压力、攻击性或强迫行为;网络平台还存在霸凌、接触不良内容等风险。在部分案例中,儿童的睡眠、学习成绩和家庭关系均受到了负面影响。
The debate reflects a bigger question: how should society understand the role of gaming in childhood development? Is it mainly a tool that helps children grow and learn, or a distraction that harms their health and well-being?
这场辩论反映了一个更宏大的问题:社会应如何看待游戏在儿童发展中的作用?它主要是帮助儿童成长和学习的工具,还是损害儿童健康与幸福感的干扰因素?
This debate is not just about games themselves—it is about what kind of childhood we want to encourage: one where technology is embraced as a learning and social tool, or one where limits are placed to protect children from risks.
这场辩论的核心不仅关乎游戏本身——更关乎我们希望倡导怎样的童年:是拥抱科技作为学习和社交工具的童年,还是通过设限来保护儿童免受风险的童年?
Prop (We support the motion)
正方(支持该辩题)
Winning Strategy:Show that games are powerful tools for learning, creativity, and social growth when used responsibly. The positives build real skills and opportunities that outweigh the manageable risks.
制胜策略:证明在合理使用的前提下,电子游戏是促进学习、激发创造力和社交成长的强大工具。其积极影响所带来的实际技能和机遇,远大于可控的风险。
Argument 论点1
Games improve cognitive skills.
游戏提升认知能力。
Claim 主张
Video games build problem-solving and critical thinking.
电子游戏能培养问题解决能力和批判性思维。
Analysis 分析
Many games require planning, strategy, and adaptability, which sharpen executive function and memory. This translates into stronger academic and real-world skills.
许多游戏需要规划、策略制定和适应能力,这些能提升执行功能和记忆力,并转化为更强的学术能力和现实生活技能。
Example 例子
A study in Nature found that children who played certain strategy games performed better in math and science tasks.
《自然》杂志的一项研究发现,玩特定策略类游戏的儿童在数学和科学任务中表现更出色。
Impact 影响
Games help raise a generation that is more capable of solving complex problems. This benefits not only the children themselves but also the rest of society by having a smarter and more creative workforce that creates economic benefits for all.
游戏有助于培养一代更善于解决复杂问题的人。这不仅对儿童自身有益,还能为社会输送更聪明、更具创造力的劳动力,进而创造经济价值,惠及全社会。

Argument 论点2
Games build social connections.
游戏构建社交联结。
Claim 主张
Online and cooperative games strengthen social skills.
在线游戏和协作类游戏能强化社交技能。
Analysis 分析
Multiplayer games require teamwork, communication, and leadership. Through the time spent, and the problems solved together, connections develop naturally over time. For shy or isolated children, online communities provide friendship and belonging.
多人游戏需要团队合作、沟通和领导力。随着共同投入时间、携手解决问题,人与人之间的联结会自然形成。对于害羞或孤僻的儿童而言,网络社区能带来友谊和归属感。
Example 例子
During the COVID-19 lockdowns, many children stayed connected through games like Minecraft and Fortnite.
新冠疫情封锁期间,许多儿童通过《我的世界》《堡垒之夜》等游戏保持联系。
Impact 影响
This reduces loneliness and builds confidence, which supports healthy social development.
这能减少孤独感、增强自信心,助力健康的社交发展。
Argument 论点3
Games support emotional resilience.
游戏培养情绪韧性。
Claim 主张
Video games teach persistence and stress management.
电子游戏能教会坚持和压力管理。
Analysis 分析
Games present challenges that require repeated effort and reward persistence. Children learn that failure is temporary and effort leads to progress.
游戏中会设置各类挑战,需要反复尝试才能完成,同时会奖励坚持不懈的行为。儿童能从中学会失败是暂时的,努力终将带来进步。
Example 例子
Research on game-based learning shows that players develop better coping strategies for frustration.
基于游戏化学习的研究表明,玩家能培养出更好的挫折应对策略。
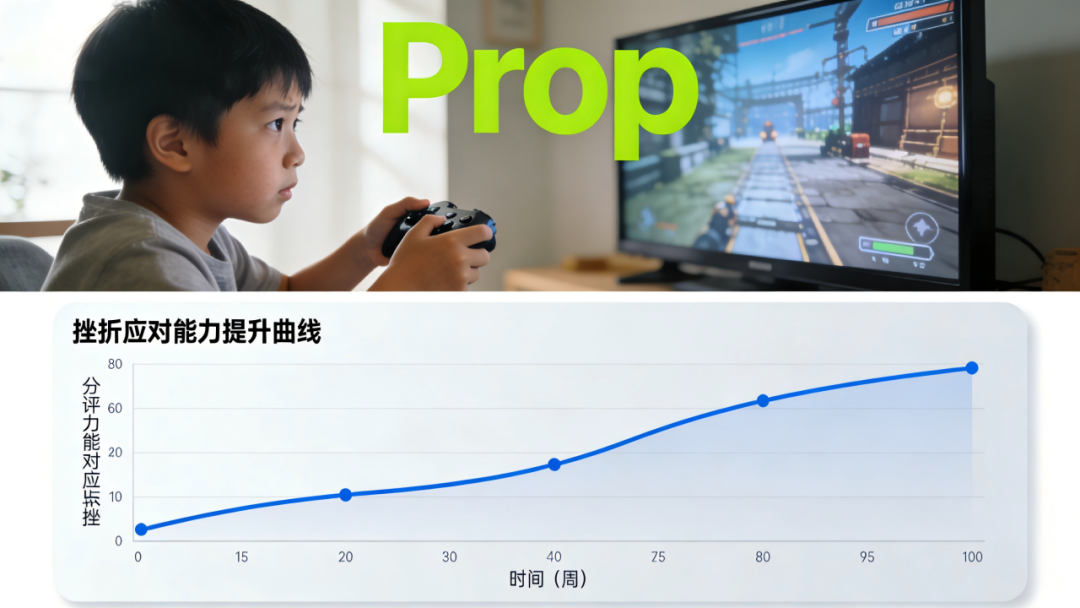
Impact 影响
Children gain resilience that helps in school, relationships, and life.
儿童获得的韧性将对其学业、人际关系和未来人生起到积极作用。
Opp (We oppose the motion)
反方(反对该议题)
Winning Strategy:Show that, in practice, the risks of gaming—addiction, lost learning time, and health harms—are widespread and outweigh potential benefits. Focus on the real-world effects rather than the ideal.
制胜策略:证明在现实中,电子游戏的风险——成瘾、学习时间流失、健康损害——普遍存在,且超过了潜在益处。聚焦实际影响而非理想状态。
Argument 论点 1
Gaming harms academic performance.
游戏损害学业表现。
Claim 主张
Games take time away from schoolwork.
游戏抢占了学业时间。
Analysis 分析
Video games, because of their high entertainment value, tend to be very addictive, especially for children whose frontal cortex has not yet fully developed. Children often play for hours, cutting into homework, reading, and sleep. Even if some games build skills, the lost study time has stronger negative effects.
电子游戏娱乐性极强,极具成瘾性,尤其对大脑前额叶皮层尚未完全发育的儿童而言。儿童常常连续玩数小时,挤占了家庭作业、阅读和睡眠时间。即便部分游戏能培养技能,流失的学习时间所带来的负面影响也更为严重。
Example例子
Studies in East Asia link heavy gaming with lower school test scores.
东亚地区的研究表明,重度游戏与较低的学业考试成绩相关。
Impact 影响
This harms children’s future opportunities and academic success.
这会损害儿童的学业成就和未来发展机遇。
Argument 论点 2
Gaming reduces physical activity and health.
游戏减少体育活动,危害健康。
Claim 主张
Long gaming sessions encourage sedentary lifestyles.
长时间游戏会导致久坐生活方式。
Analysis 分析
Children who game too much exercise less, eat poorly, and suffer sleep problems. This leads to obesity, poor fitness, and long-term health risks.
过度游戏的儿童运动更少、饮食不规律,且存在睡眠问题,进而导致肥胖、体能下降和长期健康风险。
Example 例子
The World Health Organization warns that excessive screen time is a key factor in rising childhood obesity rates.
世界卫生组织警告,屏幕使用时间过长是儿童肥胖率上升的关键因素。
Impact 影响
Poor health affects quality of life and increases healthcare costs for families and society.
健康状况不佳会影响生活质量,并增加家庭和社会的医疗成本。
Argument 论点 3
Gaming exposes children to harmful content.
游戏让儿童接触有害内容。
Claim 主张
Games often include violence, toxic behavior, or manipulative monetization.
游戏中常包含暴力元素、不良行为或诱导性消费设计。
Analysis 分析
Violent games can normalize aggression, while online platforms expose kids to bullying and predators. People who want to harm children know they play video games, so it is easy for them to infiltrate these spaces anonymously and gain children’s trust. In-game purchases pressure children into spending money irresponsibly.
暴力游戏可能使攻击性行为正常化,而网络平台让儿童面临霸凌和性侵害风险(不法分子知晓儿童热衷游戏,易匿名潜入相关空间获取信任);游戏内购机制还会迫使儿童不理性消费。
Example 例子
Reports of cyberbullying and grooming in popular online games show the dangers of unsupervised play.
有多起报告显示,热门在线游戏中存在网络霸凌和诱导性侵害的情况,凸显了无监管游戏的危险性。
Impact 影响
These risks can damage mental health and safety, leaving lasting harm on children’s development.
这些风险会损害儿童的心理健康和人身安全,对其发展造成持久伤害。
Extra Tips
额外提示
1. detailed examples of how certain games have made you learn something, helped you, or created new friendships.
正方:结合自身玩过的电子游戏,提供具体详细的例子,说明特定游戏如何让你学到知识、获得帮助或结交新朋友。
2. Opp: Use personal examples to illustrate how video games can make you sleep, study, socialize, or exercise less. Try to capture the feeling of why it is so difficult to play in moderation.
反方:用个人经历举例,说明电子游戏如何导致你睡眠减少、学习分心、社交减少或运动不足,尽量展现适度游戏的难度。
3. Find reasons why most children play video games in sustainable amounts, e.g the incentives and methods of parents.
思考多数儿童能够合理控制游戏时间的原因(如家长的引导方式和激励措施)。
4. Opp: Show how and why many families struggle to regulate their children’s video game usage and what the incentives of video game companies are for making their games as addictive as possible.
反方:阐述为何许多家庭难以监管孩子的游戏使用时间,以及游戏公司为让产品更具成瘾性所采取的激励手段。