想要在A-Level经济考试中斩获高分?关键在于掌握一套清晰、严谨的写作框架。本文以疫苗接种为例,手把手教你如何构建高分Essay——从精准定义、PEEL结构化论证,到结合图表与真实数据,再到批判性评估的进阶技巧。
据爱德思2023年考官报告(Examiners' Report June 2023 Unit 1):
多数学生在Evaluation部分仅重复KAA论点而未深入批判。“Many responses failed to develop evaluation beyond stating 'it depends on the situation'.”仅17%的答案能在评估中有效结合材料矛盾点。我们先来说一下经济Essay高分的写作框架。
Introduction
Definition & Application解释题目中的经济学术名词,并引用材料。
KAA1论点1:建议每个观点用PEEL的格式来写。
Point:给出观点。直接点题。Explanation:理论解释。结合经济模型如D&S diagram, externality diagram.Example:举例子。结合具体市场或国家分析。Link:回扣题目。解释如何支持一开始给出的观点。KAA2论点2
KAA3论点3其实2个点充分展开写清楚即可,但是如果觉得前面分析不够详细,可以接着写第三个分析点。Evaluation:批判性评估。写2-3点。常见的三种讨论点:Magnitude/size;Measurement;Time period题目问benefits/advantages可以讨论cost/disadvantages。
Conclusion
针对大分值Essay题,尤其是Discuss/ Assess开头的题目,考试有时间尽量写结论。接下来,我们来看一个具体的案例:

✅Introduction (3-4 sentences)
●Key Definitions:
Private benefits refer to direct gains to individuals (e.g., health improvement), while external benefits are positive spillovers to third parties (e.g., herd immunity).
●Contextual Hook:
Ukraine's measles cases surged from 102 (2016) to 2,381 (2017) as vaccination rates dropped from 97% (2007) to 42% (2016), demonstrating the externality implications.
●Thesis Statement:
While vaccination delivers substantial private and social benefits, its efficacy depends on data accuracy and policy design.
✅KAA1: Private Benefits (PEEL Structure)
●Point:
Vaccination reduces individual health risks and financial burdens."
●Explanation + Example:
Health Gains: Prevents measles and complications (e.g., pneumonia, encephalitis), cutting hospitalization rates (Ukraine saw 300% rise in measles admissions in 2017).
Economic Savings: WHO estimates measles treatment costs ≈5× vaccination costs per child.
●Link:
Thus, vaccination is a cost-effective private health investment.
✅KAA2: External Benefits (Diagram + Analysis)
●Point:
Vaccination generates positive externalities, notably herd immunity.
●Diagram: Label- welfare gain, under-consumption
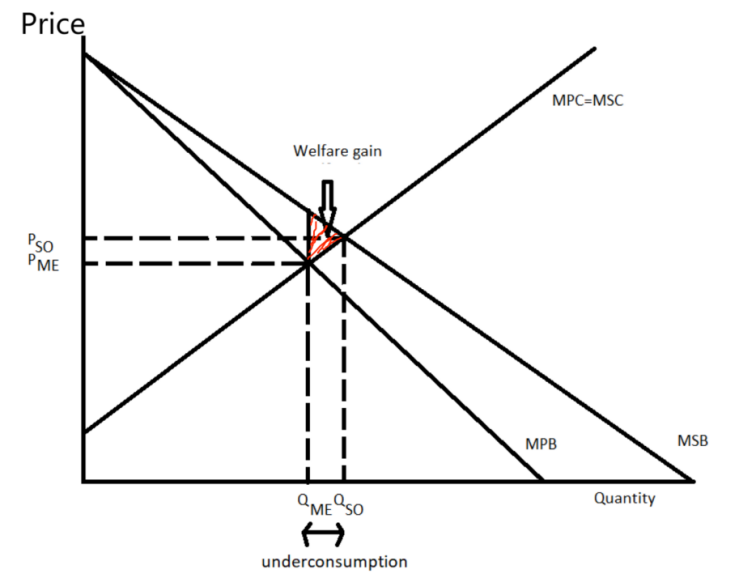
●Explanation + Example:
n Herd Immunity: CDC states 95%+ vaccination rates are needed to halt transmission — Ukraine’s 42% rate triggered outbreaks.
n Productivity:Ukraine’s Education Ministry reported 40% more student absences in 2017, reducing future workforce productivity.
●Link:
This market failure justifies government intervention (e.g., subsidies).
✅EVA1: Cost of vaccination
可以举疫苗带来的成本和社会挑战的例子,比如:疫苗费用、设施成本、强制接种引发反感。
Vaccine distribution consumed 8% of Ukraine’s 2017 health budget (World Bank), crowding out other services like maternal care
✅EVA 2: Data Reliability (Magnitude)
数据的局限性举例:由于收集问题未反映全貌分析, 从而导致误导性的决策.
Rural under-reporting may mask true vaccination rates (e.g., WHO noted 15% data gaps in Ukrainian villages), distorting policy responses
✅Conclusion 结论:好处与挑战同时存在。
In conclusion, vaccination delivers clear benefits through improved individual health and reduced disease transmission across communities. However, challenges such as unreliable vaccination data and substantial program costs require careful consideration. Addressing these issues effectively will maximize the advantages of widespread immunization.
现在,运用这个框架去练习吧——经济学的高分,始于清晰的思路与结构化的表达。